FERTILITY TREATMENTS

ASSISTED REPRODUCTION OF
HIGH COMPLEXITY
PREIMPLANTATION GENETIC DIAGNOSIS
It is a complementary genetic study applied to embryos obtained in in vitro fertilization (ICSI) that allows to show if the embryo carries a correct genetic load in terms of the number of chromosomes (PGT-A), it is also possible to determine the presence of specific diseases caused by a gene that is also present in one of the parents (PGT-M).
- To do this study, it is necessary to take a sample of the embryos obtained.
- The transfer of those embryos with normal genetic results will be performed.

CRYOPRESERVATION OF SEMEN
It is the freezing of a semen sample for a period of time that you choose.
When is it indicated to freeze a semen sample?
- Social preservation: Before vasectomy, your decision not to have any more children may change in the future.
- When a decrease in the number of spermatozoa or in the quality of the seminal sample has been observed in the spermograms, as this situation could worsen.
- Medical indications: When a major disease is detected that may affect the quality of the semen and before chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments for the treatment of cancer.

EGG VITRIFICATION
It is a technique with which we can cryopreserve eggs for long periods of time, we recommend this technique in different cases:
- To postpone motherhood: (self-preservation) In modern times, women prioritize academic, work and personal growth over motherhood, which leads to trying to have the first child at older ages, taking into account that the quantity and quality of eggs is affected by age, it is advisable to vitrify the eggs as early as possible, so that these eggs have the chronological age of freezing even if they are used many years later.
- How to preserve fertility before undergoing medical treatments such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer and other pathologies.
- When pathologies are diagnosed or you are going to undergo medical or surgical procedures that may affect your ovaries.

CRYOPRESERVATION OF EMBRYOS
The technique used for freezing is called vitrification, which results in embryo survival rates of more than 98%.
The embryos of optimal quality obtained in the in vitro fertilization treatment that are not transferred can be frozen and stored in our Bank for later attempts in case of not achieving pregnancy, or we can also thaw and transfer them when you decide to have a second baby.
The embryos can also be cryopreserved as a fertility preservation technique, to be transferred in the future.

CRYOPRESERVATION OF EGGS, SPERM AND EMBRYOS
If you are over 35 years old and have not yet made the decision to have a child, the Fertivida Scientific Center has this tool for the self-preservation of sperm, oocytes and embryos without a time limit, to be used in subsequent fertility treatments, such as inseminations or in vitro fertilization.
We have scientific personnel specialized in assisted reproduction, achieving effectiveness rates above the Latin American average.

GENETIC COMPATIBILITY TEST
This test consists of identifying in the providers of the egg and sperm gametes, genes associated with diseases that can occur in the baby in cases in which both the egg and the sperm carry the same genetic disease.
By analyzing a blood or saliva sample it is possible to detect mutations responsible for more than 500 serious genetic diseases, most individuals can be carriers of a mutation without presenting any obvious pathology, or having symptoms, when both members of the couple are carriers of the same gene there is a 25% chance that their child will have the disease.
This test can be applied to both members of the couple to find out the risk of a disease of this type, or when fertilization is going to be carried out with a gamete, whether egg or donated sperm.
Our male and female donors have the study of these genes, so it is possible to apply the genetic compatibility analysis with the donor of the other gamete, to reduce the risk of the baby inheriting serious genetic diseases from the donor and the father or mother.

EGG DONATION
It is an assisted reproduction technique in which the eggs of a donor are used to carry out the process of In Vitro Fertilization.
When is egg donation indicated?
Various conditions can affect the quality and quantity of eggs; the main one is related to age, after the age of 35 this ovarian reserve decreases until it reaches definitive failure in menopause.
- Underlying pathologies such as endometriosis that can affect the ovary.
- In cases of ovarian failure secondary to medical, pharmacological or surgical treatments.
- Genetic and chromosomal diseases can also contraindicate the use of a woman’s own eggs.
You are not alone, we will choose the best donor for you!
Who are our donors?
Donor candidates in our program go through a rigorous selection process that includes, in addition to the medical evaluation, a genetic and psychological evaluation and laboratory tests for infectious diseases, general health status and genetic tests, we also include in the process the analysis of their lifestyle habits, as well as their skills and abilities.

IN VITRO FERTILIZATION WITH SPERM INJECTION (ICSI)
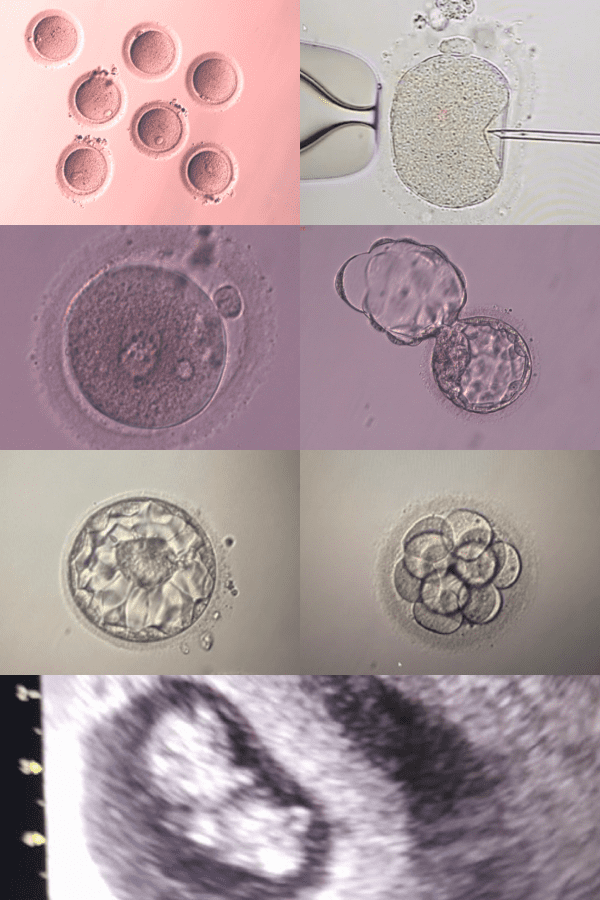
In this technique, egg fertilization occurs when we directly inject a selected sperm into each of the recovered mature eggs (ICSI), for this we use a microscope that allows magnifying the image and detailing the characteristics of the sperm and egg, it has an adapted system that allows the micromanipulation of these cells.
The embryos obtained in this technique are cultured in the laboratory for 5 or 6 days under appropriate conditions before being transferred to the uterus.
CONVENTIONAL IN VITRO FERTILIZATION (IVF)
It is a technique in which the eggs and selected sperm are placed together in a culture box for fertilization to take place.
The eggs and/or sperm can come from the partner or from a donor.
The steps to apply this technique include:
- Stimulation of the ovaries by applying medications.
- Aspiration of eggs from the ovary
- Semen sample preparation
- Approaching eggs and sperm in a culture box in the laboratory for fertilization
- Culture and follow-up of embryonic development 5 or 6 days
- Embryo transfer to uterus
ASSISTED REPRODUCTION OF
LOW COMPLEXITY
OVULATION INDUCTION
Some women have difficulty ovulating spontaneously; To make science available to them and overcome this alteration, medications are administered (taken or injected), which correct hormones and allow the ovaries to work naturally.
In other cases, increasing hormone levels in women who ovulate normally induces the maturation of more than one egg and improves the chances of achieving pregnancy either through sexual intercourse or intrauterine insemination.
INTRAUTERINE INSEMINATION
For this treatment we carry out a special preparation of the semen sample in the laboratory to improve the mobility of the spermatozoa, activating them for fertilization, the spermatozoa thus selected will be placed directly in the woman’s uterus so that fertilization occurs in her own reproductive system, for this we use a thin plastic catheter. Insemination can be:
Homologous Insemination: Sperm are from a sample of the couple’s semen.
Heterologous insemination: The seminal sample is from a donor.
For an insemination it may be necessary to slightly stimulate the ovaries and perform ultrasounds that will allow us to know the precise moment of ovulation in order to be able to perform the insemination on the most appropriate day.
INTERVENTION SURGICAL
VASECTOMY REVERSAL
Surgery that seeks to reconstruct the vas deferens (it is the one that allows the passage of sperm from the testicle to the outside) that was interrupted in the vasectomy, so that it recovers its function.
EPIDIDYMIS PUNCTURE OR TESTICULAR BIOPSY
It allows men with a total absence of sperm due to various causes, to extract them directly from the testicle or its pathways, with the purpose of using them in highly complex techniques to achieve pregnancies.
MICROSURGERY
It is an advanced surgical technique used in some cases, generally those in which the tubes are obstructed. As with the other treatments, their choice depends on the woman’s age, ovarian reserve, sperm conditions, their history and possible associated factors.
LOSS MANAGEMENT
OF PREGNANCIES
Repeated miscarriages can be caused by genetic alterations, clotting disorders, diseases of the defense system, abnormalities in their internal genital organs, infections, genetic defects in the couple or hormonal deficiencies.
The performance of modern studies will allow in most cases to establish a clear cause and a treatment according to it.
In others, some empirical measures will help to reduce the risk of a new loss, despite not having a clear cause.

